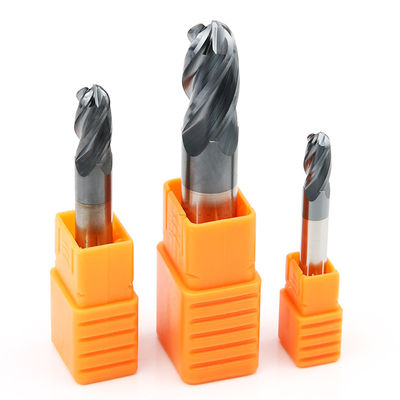
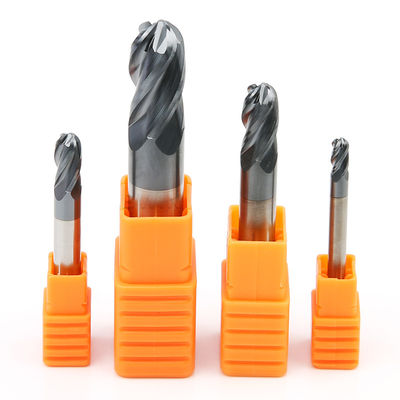
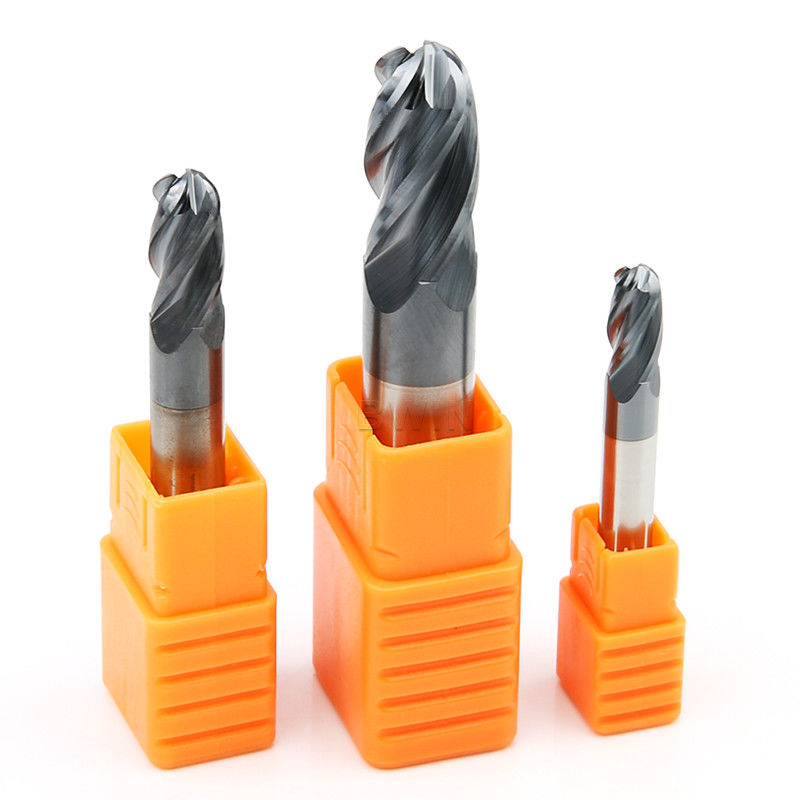
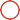
Cast iron 45 Degree End Mill Cutter Head Grooving Carbide Ball Nose End Mill
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | China |
| Brand Name: | BWIN |
| Model Number: | R1.5*6*D4*100L-4F |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1pcs/box |
|---|---|
| Price: | Negotiable |
| Packaging Details: | Plastic box |
| Delivery Time: | 7 work days |
| Payment Terms: | T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability: | 1-10000pcs 7days |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Product Name: | HRC45 4F Ball Nose Carbide End Mill | Model: | R4.5*16*D8*75L-4F Ball Nose End Mill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material: | Tungsten Steel Ball Nose Milling Cutter | Workpiece: | Cast Iron |
| Usage: | Milling Tool | Coating: | AlTiN |
| HRC: | HRC45 | Feature: | Large Core Diameter Design |
| Application: | Milling Machine | Package: | 1pcs/Box |
| Highlight: | 45 Degree End Mill Cutter Head Grooving,Carbide Ball Nose End Mill 45 Degree,Cast Iron 45 Degree End Mill Cutter |
||
Product Description
HRC45 Ball Nose Carbide End Mill Tungsten Steel Milling Cutter 4F 4 Flute Head Grooving
Characteristic:
- The ball nose carbide end mill is coated with high-quality coating, and it passes the excellent processing standard, which is sharp, wear-resistant, not easy to wear, and ensures stable performance and safety;
- The large core diameter design and hardening treatment enhance the rigidity and vibration resistance of the tool, which is sturdy and durable, shock resistant and stable. The cutting edge is nano coated, which is fast in cutting speed and reduces the number of tool changes;
- Chamfering design saves the time of tool replacement, greatly improves the processing efficiency, and has a wide range of applications. It can be used for plane processing, side processing, grooving, U-groove processing, etc.
Description:
- Fine grinding spiral groove, large chip removal, avoiding chip accumulation, high precision and more luster, greatly improving processing efficiency;
- The design of large core diameter is adopted under the condition of ensuring the cutting space, which greatly enhances the rigidity and seismic resistance of the tool, reduces tool breakage, and makes the performance more stable; Four edge ball head design of ball nose carbide end mill is applicable to semi finishing and finishing of various curved surfaces and arc grooves; Small ball end milling cutter can finish milling small chamfers of steep wall/straight wall and irregular contour surface; The universal chamfered round handle design is convenient to use and has good compatibility. It can enhance the shock resistance and cutting speed of the milling cutter, and it can be clamped more tightly without slipping.
Milling parameters:
| HRC45 Carbide End Mill |
Tool length | fz&v | |||||
| Short |
1 |
||||||
| Long1 | 0.9 | ||||||
| Overlength | 0.8 | ||||||
| Speciality | 0.6 | ||||||
| Type | Material |
Strength N/mm²
Hardness HRC |
Cooling | ||||
| Air |
Dry cutting |
Lubricating fluid | |||||
| P | PI |
P1.1 |
Non alloy structural steel, free cutting structural steel, carburized steel and quenched and tempered steel | <700 | √ | √ | √ |
| P1.2 | quenched and tempered steel | <1200 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| P2 | P2.1 | Alloyed nitrided steel, carburized steel and quenched and tempered steel | <900 | √ | √ | √ | |
| P2.2 | Tool steel, bearing steel, spring steel and high-speed steel | <1400 | √ | √ | |||
| P3 | P3.1 | Tool steel, bearing steel, spring steel and high-speed steel | <900 | √ | √ | √ | |
| P3.2 | Tool steel, bearing steel, spring steel and high-speed steel | <1500 | √ | √ | |||
| Sloting | ||||||||||||
| Vc (m/min) |
fz(mm/Tooth) | |||||||||||
| Diameter | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 | |||||
| 112 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 0.048 | 0.06 | 0.069 | ||||
| 92 | 0.01 | 0.017 | 0.025 | 0.032 | 0.038 | 0.045 | 0.056 | 0.065 | ||||
| 100 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 0.048 | 0.06 | 0.069 | ||||
| 72 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.022 | 0.028 | 0.034 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.058 | ||||
| 64 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.025 | 0.032 | 0.039 | 0.045 | 0.057 | 0.066 | ||||
| 56 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.052 | 0.06 | ||||
| Roughing | ||||||||||||
| Vc (m/min) |
fz(mm/Tooth) | |||||||||||
| Diameter | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 | |||||
| 228 | 0.018 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.057 | 0.070 | 0.081 | 0.101 | 0.118 | ||||
| 208 | 0.017 | 0.029 | 0.042 | 0.054 | 0.065 | 0.071 | 0.095 | 0.11 | ||||
| 184 | 0.018 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.057 | 0.070 | 0.081 | 0.101 | 0.118 | ||||
| 144 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.037 | 0.048 | 0.058 | 0.068 | 0.085 | 0.098 | ||||
| 132 | 0.017 | 0.03 | 0.042 | 0.054 | 0.066 | 0.077 | 0.096 | 0.112 | ||||
| 112 | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.039 | 0.05 | 0.060 | 0.07 | 0.088 | 0.102 | ||||
| Finish | |||||||||||
| Vc m/min |
fz(mm/Tooth) | ||||||||||
| Diameter | |||||||||||
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | ||
| 332 | 0.028 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.091 | 0.11 | 0.128 | 0.144 | 0.16 | 0.173 | 0.186 | |
| 272 | 0.026 | 0.046 | 0.066 | 0.085 | 0.103 | 0.12 | 0.135 | 0.15 | 0.162 | 0.173 | |
| 304 | 0.028 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.091 | 0.11 | 0.128 | 0.144 | 0.16 | 0.173 | 0.186 | |
| 212 | 0.023 | 0.041 | 0.059 | 0.076 | 0.092 | 0.107 | 0.121 | 0.134 | 0.145 | 0.155 | |
| 196 | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.067 | 0.086 | 0.104 | 0.122 | 0.137 | 0.152 | 0.165 | 0.177 | |
| 168 | 0.024 | 0.043 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.125 | 0.139 | 0.150 | 0.161 | |
- If the following carbide end mill cannot meet your requirements, we support OEM customized production. The diameter of 0.2mm to 25mm, the total length of 50mm to 200mm, 4F, 5F, 6F, 8F and logo can be customized, including inch size end milling cutter. Please contact us to select or customize non-standard carbide end mill according to your needs.
| Specification | Flute Radius | Flute Length (C) | Shank Radius | Overall Length(L) |
| R0.5*2*d4*50L |
0.5 |
2 |
4 |
50 |
|
R0.75*3*d4*50L |
0.75 |
3 |
4 |
50 |
|
R1*4*d4*50L |
1 |
4 |
4 |
50 |
|
R1.25*5*d4*50L |
1.25 |
5 |
4 |
50 |
|
R1.5*6*d4*50L |
1.5 |
6 |
4 |
50 |
|
R1.75*7*d4*50L |
1.75 |
7 |
4 |
50 |
|
R2*8*d4*50L |
2 |
8 |
4 |
50 |
|
R2.5*10*d5*50L |
2.5 |
10 |
5 |
50 |
|
R3*12*d6*50L |
3 |
12 |
6 |
50 |
|
R4*16*d8*60L |
4 |
16 |
8 |
60 |
|
R5*20*d10*75L |
5 |
20 |
10 |
75 |
|
R6*24*d12*100L |
6 |
24 |
12 |
100 |
|
R7*28*d14*150L |
7 |
28 |
14 |
150 |
|
R8*32*d16*100L |
8 |
32 |
16 |
100 |
|
R9*36*d18*100L |
9 |
36 |
18 |
100 |
|
R10*40*d20*100L |
10 |
40 |
20 |
100 |
- Minimize the use of tool tips to process workpieces: at the position of the ball head tool tip, the processing linear speed is 0 during actual processing, that is, the tool is not actually cutting, but grinding. In actual processing, the coolant can not be added to the cutting area at all, which further leads to greater cutting heat ratio and reduced tool life.
- For the straight wall, use the contour processing method to process: try to reduce the ball end cutter downward along the straight wall.The phenomenon of processing. Relatively speaking, it is a very good method to process upward along the straight wall, but it is difficult to separate them in actual processing. Let's compare the differences between the two.
- Machining straight wall with contour can reduce downward machining. If you can use "cutting from bottom to top", this phenomenon can be avoided. When using "cutting from bottom to top", first consider whether the cutting capacity of the cutter is too large. If there are relatively large residues left at the root of the curved surface after machining above, the cutting capacity of the cutter may be too large. This will not protect the tool but destroy it.
- The ball end milling cutter shall pay attention to the processing of deep grooves: when processing deep grooves, the cutter may sink. Because the chip holding groove of the ball end milling cutter is relatively small, it is easy to break the cutter when processing sticky materials (such as red copper) and the feed speed is fast. Therefore, pay attention to chip removal when using ball end cutter for machining.
Applications:
- Pre-hardened Steel, stainless steel, Die steel, steel plate, Heat-resistant steel,pipe, copper and aluminum, cast iron, Nonferrous Metal, Wood, Plastic,FRP and sO on. General-purpose operation slotting, rilling, profiling.
![]()
Q1. The tool breaks when cutting in or pulling out the workpiece
The feed rate and cutting depth can be reduced, and the cutting edge length can be shortened to the minimum of the necessary length.
Q2. Tool breaks during normal machining
Reduce the feed rate and cutting depth.
The tool shall be passivated.
Replace the clamp or spring collet.
The tool with high cutting edge number changes the tool with low cutting edge number to improve chip removal and prevent chip blockage.
Replace dry milling with wet milling (using cutting fluid), and use it with vortex tube gun to reduce tool temperature and avoid tool overheating.
If the wet milling fluid supply direction is changed from the front to the oblique rear or transverse top, the coolant flow should be sufficient.
Q3. The tool breaks when the feed direction changes
(1) Use arc interpolation (NC machine tool), or temporarily stop (temporarily) feeding.
(2) Reduce (decrease) the feed before and after the direction change.
(3) Replace the clamp or spring collet.
Q4. Problem: Part of the blade tip breaks
Chamfer the corners with manual grinding.
Change down milling to up milling.